Pancreatitis is a condition that should grab the attention of every dog owner. It poses a risk, to our furry companions if not handled correctly.…

Pet Grooming Dogs, Cats, Rats, Turtles and many other animals

Pancreatitis is a condition that should grab the attention of every dog owner. It poses a risk, to our furry companions if not handled correctly.…

Hello, dear dog lovers! We value the joy that our furry friends bring into our lives as pet owners. However, it is essential that you…

I feel an inexplicable bond with my canine companion. The wagging tail, the soulful eyes – they speak a language of love beyond words. But,…

Ticks are a common problem that many dog owners face. These tiny, blood-sucking parasites can be found in various environments and can pose a threat…

As devoted pet owners, our dogs hold a special place in our hearts and homes. However, amidst all the love and joy they bring, our…

Worm infestations are a common health concern for dogs, and it’s vital for pet owners to be aware of the symptoms associated with these parasites.…

Dogs are beloved members of many families, providing companionship, protection, and unconditional love. However, just like humans, dogs are vulnerable to a range of health…
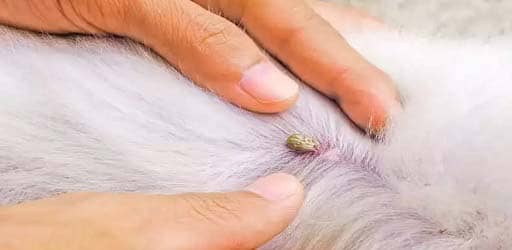
Our lovely furry friend contracted a disease is the last thing any dog owner wishes. Especially if it can create discomfort and make the dog…
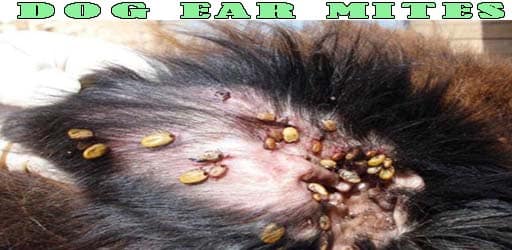
Dog is a lovely furry friend to keep you company. Aside from its cuteness and unhinged loyalty, there are threats from the outside that may…
Our canine companions bring immense joy and love into our lives. However, just like us, dogs are susceptible to various health conditions. As responsible pet owners, it’s crucial to be aware of the common diseases that can affect our four-legged friends.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore several prevalent diseases in dogs, including ear infections, doggy diarrhea, distemper, parvovirus, fleas and ticks, cataracts, hypothyroidism, hip dysplasia, elbow dysplasia, and obesity.
We understand the importance of providing you with accurate and detailed information to ensure the well-being of your beloved canine companions. Let’s talk about a range of common diseases that can affect dogs, along with their symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures.
Dog ear infections are a frequent health issue in dogs, particularly those with floppy ears or excessive hair in the ear canals. If left untreated, ear infections can lead to more severe complications.
Causes: Bacteria, yeast, or allergies can cause these infections.
Symptoms: Symptoms of an ear infection include
Treatment: Treatment typically involves cleaning the ears and administering medication prescribed by a veterinarian. Prompt veterinary care is necessary to diagnose and treat the infection effectively.
Diarrhea is a common digestive problem in dogs and can have various causes
Causes: Common causes include dietary indiscretion, sudden diet changes, bacterial or viral infections, intestinal parasites, or underlying health conditions.
Symptoms: Symptoms include
Treatment and Management: In most cases, doggy diarrhea resolves on its own within a day or two. However, if it persists or is accompanied by other concerning symptoms, a visit to the veterinarian is recommended. Treatment may involve dietary modifications, medication, and ensuring proper hydration.
Ticks and fleas on dogs are external parasites that can cause significant discomfort and health problems in dogs. Fleas are small insects that infest a dog’s fur, leading to itching, skin irritation, and even allergies. Ticks, on the other hand, attach themselves to a dog’s skin and feed on their blood. They can cause discomfort and transmit diseases to dogs.
Treatment and Management: Regular use of flea and tick preventatives and thorough grooming and inspections after outdoor activities are crucial in preventing infestations and disease transmission.
Cataracts are a common eye condition in dogs, characterized by the clouding of the lens. Cataracts can develop gradually or progress rapidly, and they may affect one or both eyes. It can cause vision impairment or even blindness if left untreated.
Causes: They can develop as a result of aging, genetics, trauma, or underlying health conditions such as diabetes.
Treatment: Surgery may be necessary to remove cataracts and restore vision in affected dogs.
Mange in dogs is a common skin condition caused by mites that infest the skin and hair follicles of dogs. The two most common types of mange seen in dogs are sarcoptic mange and demodectic mange.
Symptoms: Common signs of mange in dogs include
Veterinary care is essential for an accurate diagnosis, as well as to determine the appropriate treatment options. With proper care and management, dogs with mange can find relief and regain healthy skin.
Dog worms are a common concern among pet owners, with various types posing health risks to our furry friends. One of the most prevalent types is roundworms in dogs. These intestinal parasites can be found in the digestive tract, and their eggs can be shed in dog poop. Dogs may acquire roundworms by ingesting the eggs from contaminated soil, water, or infected animals.
Another type of worm frequently encountered is hookworms in dogs. These parasites attach themselves to the intestinal wall and feed on the dog’s blood, causing anemia and gastrointestinal distress. Tapeworms reside in the dog’s intestines and can be contracted by ingesting fleas or small mammals infested with tapeworm larvae.
Heartworms in dogs pose a significant health risk and are transmitted through mosquito bites. The larvae enter the dog’s bloodstream and develop into adult worms that reside in the heart and lungs. If left untreated, heartworm disease can be fatal. To safeguard your canine companions, regular deworming is essential.
Canine distemper is a highly contagious viral disease that affects dogs’ respiratory, gastrointestinal, and nervous systems. It spreads through airborne exposure to infected respiratory secretions.
Symptoms: Early signs of distemper include
As the disease progresses, it can lead to neurological symptoms, such as seizures and paralysis.
Treatment and Management: Vaccination is the best defense against parvovirus, along with proper hygiene and avoiding contact with infected dogs. Prompt veterinary care is essential for infected dogs.
Canine parvovirus is a highly contagious viral infection that primarily affects puppies and unvaccinated dogs. Parvovirus attacks rapidly dividing cells in the dog’s body, primarily affecting the gastrointestinal tract and bone marrow.
Causes: It is transmitted through contact with infected feces or contaminated environments.
Symptoms: Symptoms include severe
Treatment: Treatment involves intensive veterinary care to manage symptoms and prevent secondary infections. Vaccination, proper hygiene practices, and avoiding contact with infected dogs are key preventive measures.
The thyroid gland plays a vital role in regulating metabolism, growth, and overall body function. Hypothyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone.
Symptoms: Hypothyroidism can result in a variety of symptoms, including
Treatment and Management: Hypothyroidism is typically managed with lifelong medication to replace the deficient thyroid hormone.
Hip dysplasia is a common orthopedic condition that affects the hip joint in dogs. This condition can lead to joint instability, inflammation, and subsequent degenerative changes, causing pain and mobility issues for affected dogs. Large and giant breed dogs are more prone to hip dysplasia, although it can affect dogs of any size.
Symptoms: Symptoms include
Treatment: Treatment for hip dysplasia may vary depending on the severity of the condition and the individual dog. Treatment options range from medication and weight management to physical therapy and surgical interventions.
Similar to hip dysplasia, elbow dysplasia is an orthopedic condition that affects the elbow joint in dogs. It is caused by abnormal growth and development of the elbow joint, leading to joint incongruity and subsequent damage to the surrounding structures. Large and medium-sized breeds, especially those prone to rapid growth, are more susceptible to elbow dysplasia.
Symptoms: Symptoms include
Treatment: Treatment may involve medications, physical therapy, and in severe cases, surgery.
Obesity is a prevalent health issue affecting dogs worldwide. It occurs when a dog’s body weight exceeds the ideal range, primarily due to excessive calorie intake and lack of physical activity. Obesity can lead to various health problems, including joint issues, diabetes, heart disease, and decreased life expectancy.
Management: Managing a dog’s weight through a balanced diet, portion control, and regular exercise is essential to prevent and address obesity.
As dog owners, it is important to educate ourselves about the common diseases that can affect our furry companions. By being aware of the symptoms, preventive measures, and treatment options, we can provide them with the best care possible. Regular veterinary check-ups, vaccinations, proper hygiene practices, and a nutritious diet are key to maintaining their health and happiness.